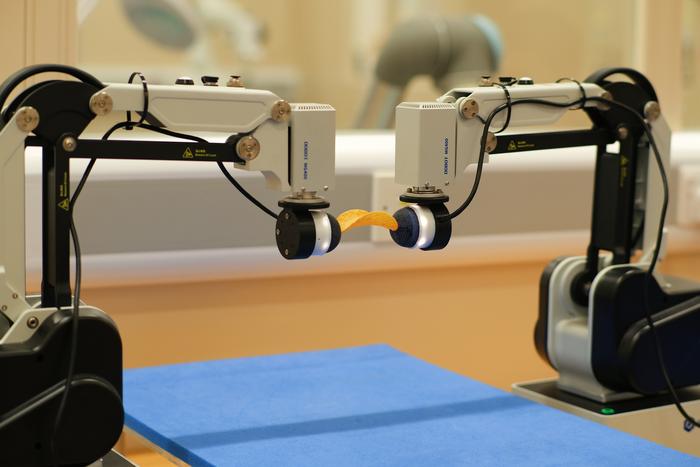
An innovative bimanual robot developed by a researchers in the UK demonstrates tactile sensitivity close to human-level dexterity, using AI to inform its actions.
Copyright: htworld.co.uk – “Dual-Arm Robot Could Recreate Touch in Artificial Limbs”

The new Bi-Touch system, designed by researchers at the University of Bristol and based at the Bristol Robotics Laboratory, allows robots to carry out manual tasks by sensing what to do from a digital helper.
The research shows how an AI agent interprets its environment through tactile and proprioceptive feedback, and then control the robots’ behaviours, enabling precise sensing, gentle interaction and effective object manipulation to accomplish robotic tasks.
This development could revolutionise industries such as fruit picking, domestic service and eventually recreate touch in artificial limbs.
Lead author Yijiong Lin from the Faculty of Engineering, said: “With our Bi-Touch system, we can easily train AI agents in a virtual world within a couple of hours to achieve bimanual tasks that are tailored towards the touch.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe to our AI NAVIGATOR!
“And more importantly, we can directly apply these agents from the virtual world to the real world without further training.
“The tactile bimanual agent can solve tasks even under unexpected perturbations and manipulate delicate objects in a gentle way.”
Bimanual manipulation with tactile feedback is key to human-level robot dexterity.
However, the topic is less explored than single-arm settings, partly due to the availability of suitable hardware along with the complexity of designing effective controllers for tasks with relatively large state-action spaces.
The researchers were able to develop a tactile dual-arm robotic system using recent advances in AI and robotic tactile sensing.[…]
Read more: www.htworld.co.uk

An innovative bimanual robot developed by a researchers in the UK demonstrates tactile sensitivity close to human-level dexterity, using AI to inform its actions.
Copyright: htworld.co.uk – “Dual-Arm Robot Could Recreate Touch in Artificial Limbs”
The new Bi-Touch system, designed by researchers at the University of Bristol and based at the Bristol Robotics Laboratory, allows robots to carry out manual tasks by sensing what to do from a digital helper.
The research shows how an AI agent interprets its environment through tactile and proprioceptive feedback, and then control the robots’ behaviours, enabling precise sensing, gentle interaction and effective object manipulation to accomplish robotic tasks.
This development could revolutionise industries such as fruit picking, domestic service and eventually recreate touch in artificial limbs.
Lead author Yijiong Lin from the Faculty of Engineering, said: “With our Bi-Touch system, we can easily train AI agents in a virtual world within a couple of hours to achieve bimanual tasks that are tailored towards the touch.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe to our AI NAVIGATOR!
“And more importantly, we can directly apply these agents from the virtual world to the real world without further training.
“The tactile bimanual agent can solve tasks even under unexpected perturbations and manipulate delicate objects in a gentle way.”
Bimanual manipulation with tactile feedback is key to human-level robot dexterity.
However, the topic is less explored than single-arm settings, partly due to the availability of suitable hardware along with the complexity of designing effective controllers for tasks with relatively large state-action spaces.
The researchers were able to develop a tactile dual-arm robotic system using recent advances in AI and robotic tactile sensing.[…]
Read more: www.htworld.co.uk
Share this: